- yj =
2u2j-1-1
- zj = 2u2j-1
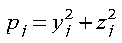
If pj >= 1, then pj is discarded, and steps 1 through 3 are repeated until pj < 1.
- x2j-1 = yj
((-2 ln pj) /
pj)0.5
- x2j = zj ((-2 ln pj) / pj)0.5
- for j = 1, n/2
- x2j = zj ((-2 ln pj) / pj)0.5

These subroutines generate vector x of normally distributed
pseudo-random numbers, with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1, using
Polar methods with a user-specified seed.
| x, aux | seed | Subroutine |
| Short-precision real | Long-precision real | SNRAND |
| Long-precision real | Long-precision real | DNRAND |
| Fortran | CALL SNRAND | DNRAND (seed, n, x, aux, naux) |
| C and C++ | snrand | dnrand (seed, n, x, aux, naux); |
| PL/I | CALL SNRAND | DNRAND (seed, n, x, aux, naux); |
If naux = 0 and error 2015 is unrecoverable, aux is ignored.
Otherwise, it is the storage work area used by this subroutine. Its size must be greater than or equal to n/2.
Specified as: an area of storage, containing numbers of the data type indicated in Table 169. They can have any value.
If naux = 0 and error 2015 is unrecoverable, SNRAND and DNRAND dynamically allocate the work area used by the subroutine. The work area is deallocated before control is returned to the calling program.
Otherwise, naux >= n/2.
The normally distributed pseudo-random numbers, with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1, are generated as follows, using Polar methods with a user-specified seed. The Polar method, which this technique is based on, was developed by G. E. P. Box, M. E. Muller, and G. Marsaglia and is described in reference [76].
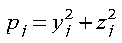
If pj >= 1, then pj is discarded, and steps 1 through 3 are repeated until pj < 1.
If n is 0, no computation is performed, and the initial seed is unchanged.
Error 2015 is unrecoverable, naux = 0, and unable to allocate work area.
None
This example shows a call to SNRAND to generate 10 random numbers.
SEED N X AUX NAUX
| | | | |
CALL SNRAND( SEED , 10 , X , AUX , 5 )
SEED = 80629.0
SEED = 48669425.0
X = (0.660649538,
1.312503695,
1.906438112,
0.014065863,
-0.800935328,
-3.058144093,
-0.397426069,
-0.370634943,
-0.064151444,
-0.275887042)
This example shows a call to DNRAND to generate 10 random numbers.
SEED N X AUX NAUX
| | | | |
CALL DNRAND( SEED , 10 , X , AUX , 5 )
SEED = 80629.0
SEED = 48669425.0
X = (0.6606495655963802,
1.3125037758861060,
1.9064381379483730,
0.0140658628770495,
-0.8009353314494653,
-3.0581441239248530,
-0.3974260845722100,
-0.3706349643478605,
-0.0641514443372939,
-0.2758870630332470)