Writing Assembler Code
On Compaq Tru64 UNIX, RS/6000 IBM AIX, and SGI IRIX operating systems, TotalView lets you use assembler code in evaluation points, conditional breakpoints, and in the Tools > Evaluate dialog box. However, if you want to use assembler constructs, you must enable compiled expressions. See Interpreted vs. Compiled Expressions for instructions.
To indicate that an expression in the breakpoint or Evaluate dialog box is an assembler expression, click on the Assembler button in the Action Point > Properties dialog box, as shown in the following figure.
Using Assembler 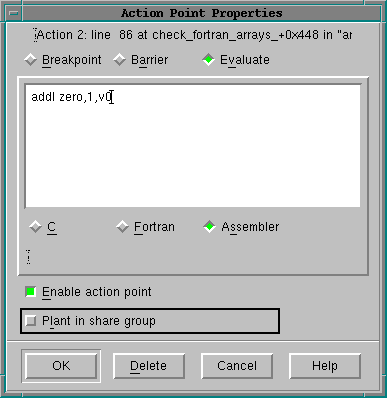
|
Assembler expressions are written in the TotalView Assembler Language. In this language, instructions are written in the target machine's native assembler language; the operators available to construct expressions in instruction operands and the set of available pseudo-operators, however, are the same on all machines.
The TotalView assembler accepts instructions using the same mnemonics recognized by the native assembler and recognizes the same names for registers that native assemblers recognize.
Some architectures provide extended mnemonics that do not correspond exactly with machine instructions and which represent important, special cases of instructions, or provide for assembling short, commonly used sequences of instructions. The TotalView assembler recognizes these mnemonics if:
- They assemble to exactly one instruction.
- The relationship between the operands of the extended mnemonics and the fields in the assembled instruction code is a simple one-to-one correspondence.
Assembler Language, labels are indicated as name: and appear at the beginning of a line. Labels may appear alone on a line. The symbols you can use include labels defined in the assembler expression and all program symbols.
The TotalView assembler operators are described in the following table:
| Operators |
Definition |
| + |
Plus |
| - |
Minus (also unary) |
| * |
Times |
| # |
Remainder |
| / |
Quotient |
| & |
Bitwise AND |
| ^ |
Bitwise XOR |
| ! |
Bitwise OR NOT (also unary -, bitwise NOT) |
| | |
Bitwise OR |
| (expr) |
Grouping |
| << |
Left shift |
| >> |
Right shift |
| "text" |
Text string, 1-4 characters long, is right justified in a 32-bit word |
| hi16 (expr) |
Low 16 bits of operand expr |
| hi32 (expr) |
High 32 bits of operand expr |
| lo16 (expr) |
High 16 bits of operand expr |
| lo32 (expr) |
Low 32 bits of operand expr |
The TotalView Assembler pseudo-operations are as follows:
| Pseudo Ops |
Definition |
| $debug [ 0 | 1 ] |
Internal debugging option.
With no operand, toggle debugging;
0 => turn debugging off
1 => turn debugging on |
| $hold
$holdprocess |
Hold the process |
| $holdstopall
$holdprocessstopall |
Hold the process and stop the control group |
| $holdthread |
Hold the thread |
| $holdthreadstop
$holdthreadstopprocess |
Hold the thread and stop process |
| $holdthreadstopall |
Hold the thread and stop the control group |
| $long_branch expr |
Branch to location expr using a single instruction in an architecture-independent way; using registers is not required |
| $stop
$stopprocess |
Stop the process |
| $stopall |
Stop the control group |
| $stopthread |
Stop the thread |
| name=expr |
Same as def name,expr |
| align expr [, expr ] |
Align location counter to an operand 1 alignment; use operand 2 (or zero) as the fill value for skipped bytes |
| ascii string |
Same as string |
| asciz string |
Zero-terminated string |
| bss name,size-expr[,expr] |
Define name to represent size-expr bytes of storage in the bss section with alignment optional expr; the default alignment depends on the size: if size-expr >= 8 then 8 else
if size-expr >= 4 then 4 else
if size-expr >= 2 then 2 else 1 |
| byte expr [, expr ] ... |
Place expr values into a series of bytes |
| comm name,expr |
Define name to represent expr bytes of storage in the bss section; name is declared global; alignment is as in bss without an alignment argument |
| data |
Assemble code into data section (data) |
| def name,expr |
Define a symbol with expr as its value |
| double expr [, expr ] ... |
Place expr values into a series of doubles |
| equiv name,name |
Make operand 1 be an abbreviation for operand 2 |
| fill expr, expr, expr |
Fill storage with operand 1 objects of size operand 2, filled with value operand 3 |
| float expr [, expr ] ... |
Place expr values into a series of floats |
| global name |
Declare name as global |
| half expr [, expr ] ... |
Place expr values into a series of 16-bit words |
| lcomm name,expr[,expr] |
Identical to bss |
| lsym name,expr |
Same as def name,expr but allows redefinition of a previously defined name |
| org expr [, expr ] |
Set location counter to operand 1 and set operand 2 (or zero) to fill skipped bytes |
| quad expr [, expr ] ... |
Place expr values into a series of 64-bit words |
| string string |
Place string into storage |
| text |
Assemble code into text section (code) |
| word expr [, expr ] ... |
Place expr values into a series of 32-bit words |
| zero expr |
Fill expr bytes with zeros |