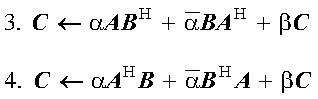

These subroutines compute one of the following rank-2k updates, where matrix C is stored in upper or lower storage mode. SSYR2K, DSYR2K, CSYR2K, and ZSYR2K use the scalars alpha and beta, real or complex matrices A and B or their transposes, and real or complex symmetric matrix C to compute:
CHER2K and ZHER2K use the scalars alpha and beta, complex matrices A and B or their complex conjugate transposes, and complex Hermitian matrix C to compute:
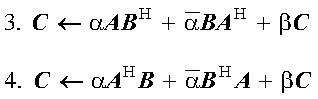
| A, B, C, alpha | beta | Subprogram |
| Short-precision real | Short-precision real | SSYR2K |
| Long-precision real | Long-precision real | DSYR2K |
| Short-precision complex | Short-precision complex | CSYR2K |
| Long-precision complex | Long-precision complex | ZSYR2K |
| Short-precision complex | Short-precision real | CHER2K |
| Long-precision complex | Long-precision real | ZHER2K |
| Fortran | CALL SSYR2K | DSYR2K | CSYR2K | ZSYR2K | CHER2K | ZHER2K (uplo, trans, n, k, alpha, a, lda, b, ldb, beta, c, ldc) |
| C and C++ | ssyr2k | dsyr2k | csyr2k | zsyr2k | cher2k | zher2k (uplo, trans, n, k, alpha, a, lda, b, ldb, beta, c, ldc); |
| PL/I | CALL SSYR2K | DSYR2K | CSYR2K | ZSYR2K | CHER2K | ZHER2K (uplo, trans, n, k, alpha, a, lda, b, ldb, beta, c, ldc); |
If uplo = 'U', C is stored in upper storage mode.
If uplo = 'L', C is stored in lower storage mode.
Specified as: a single character. It must be 'U' or 'L'.
If trans = 'N', A and B are used, resulting in equation 1 or 3.
If trans = 'T', AT and BT are used, resulting in equation 2.
If trans = 'C', AH and BH are used, resulting in equation 4.
Specified as: a single character, where:
For SSYR2K and DSYR2K, it must be 'N', 'T', or 'C'.
For CSYR2K and ZSYR2K, it must be 'N' or 'T'.
For CHER2K and ZHER2K, it must be 'N' or 'C'.
If trans = 'N', then n <= lda and n <= ldb.
If trans = 'N', it is the number of columns in matrices A and B.
If trans = 'T' or 'C', it is the number of rows in matrices A and B.
Specified as: a fullword integer; k >= 0 and:
If trans = 'T' or 'C', then k <= lda and k <= ldb.
If trans = 'N', A is n by k.
If trans = 'T' or 'C', A is k by n.
Specified as: a two-dimensional array, containing numbers of the data type indicated in Table 80, where:
If trans = 'N', its size must be lda by (at least) k.
If trans = 'T' or 'C', its size must be lda by (at least) n.
If trans = 'N', lda >= n.
If trans = 'T' or 'C', lda >= k.
If trans = 'N', B is n by k.
If trans = 'T' or 'C', B is k by n.
Specified as: a two-dimensional array, containing numbers of the data type indicated in Table 80, where:
If trans = 'N', its size must be ldb by (at least) k.
If trans = 'T' or 'C', its size must be ldb by (at least) n.
If trans = 'N', ldb >= n.
If trans = 'T' or 'C', ldb >= k.
If uplo = 'U', C is stored in upper storage mode.
If uplo = 'L', C is stored in lower storage mode.
Specified as: an ldc by (at least) n array, containing numbers of the data type indicated in Table 80.
If uplo = 'U', C is stored in upper storage mode.
If uplo = 'L', C is stored in lower storage mode.
Returned as: an ldc by (at least) n array, containing numbers of the data type indicated in Table 80.
These subroutines can perform the following rank-2k updates. For SSYR2K and DSYR2K, matrix C is real symmetric. For CSYR2K and ZSYR2K, matrix C is complex symmetric. They perform:
For CHER2K and ZHER2K, matrix C is complex Hermitian. They perform:
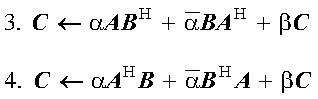
where:
See references [32], [38], and [72]. In the following two cases, no computation is performed:
Assuming the above conditions do not exist, if beta is not one, and alpha is zero or k is zero, then betaC is returned.
Unable to allocate internal work area.
None
This example shows the computation C<--alphaABT+alphaBAT+betaC, where A and B are 8 by 2 real rectangular matrices, and C is a real symmetric matrix of order 8, stored in upper storage mode.
UPLO TRANS N K ALPHA A LDA B LDB BETA C LDC
| | | | | | | | | | | |
CALL SSYR2K( 'U' , 'N' , 8 , 2 , 1.0 , A , 9 , B , 8 , 1.0 , C , 10 )
* *
| 0.0 8.0 |
| 1.0 9.0 |
| 2.0 10.0 |
| 3.0 11.0 |
A = | 4.0 12.0 |
| 5.0 13.0 |
| 6.0 14.0 |
| 7.0 15.0 |
| . . |
* *
* *
| 15.0 7.0 |
| 14.0 6.0 |
| 13.0 5.0 |
B = | 12.0 4.0 |
| 11.0 3.0 |
| 10.0 2.0 |
| 9.0 1.0 |
| 8.0 0.0 |
* *
* *
| 0.0 1.0 3.0 6.0 10.0 15.0 21.0 28.0 |
| . 2.0 4.0 7.0 11.0 16.0 22.0 29.0 |
| . . 5.0 8.0 12.0 17.0 23.0 30.0 |
| . . . 9.0 13.0 18.0 24.0 31.0 |
C = | . . . . 14.0 19.0 25.0 32.0 |
| . . . . . 20.0 26.0 33.0 |
| . . . . . . 27.0 34.0 |
| . . . . . . . 35.0 |
| . . . . . . . . |
| . . . . . . . . |
* *
* *
| 112.0 127.0 143.0 160.0 178.0 197.0 217.0 238.0 |
| . 138.0 150.0 163.0 177.0 192.0 208.0 225.0 |
| . . 157.0 166.0 176.0 187.0 199.0 212.0 |
| . . . 169.0 175.0 182.0 190.0 199.0 |
C = | . . . . 174.0 177.0 181.0 186.0 |
| . . . . . 172.0 172.0 173.0 |
| . . . . . . 163.0 160.0 |
| . . . . . . . 147.0 |
| . . . . . . . . |
| . . . . . . . . |
* *
This example shows the computation C<--alphaATB+alphaBTA+betaC, where A and B are 3 by 8 real rectangular matrices, and C is a real symmetric matrix of order 8, stored in lower storage mode.
UPLO TRANS N K ALPHA A LDA B LDB BETA C LDC
| | | | | | | | | | | |
CALL SSYR2K( 'L' , 'T' , 8 , 3 , 1.0 , A , 4 , B , 5 , 1.0 , C , 8 )
* *
| 0.0 3.0 6.0 9.0 12.0 15.0 18.0 21.0 |
A = | 1.0 4.0 7.0 10.0 13.0 16.0 19.0 22.0 |
| 2.0 5.0 8.0 11.0 14.0 17.0 20.0 23.0 |
| . . . . . . . . |
* *
* *
| 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 |
| 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 |
B = | 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 |
| . . . . . . . . |
| . . . . . . . . |
* *
* *
| 0.0 . . . . . . . |
| 1.0 8.0 . . . . . . |
| 2.0 9.0 15.0 . . . . . |
C = | 3.0 10.0 16.0 21.0 . . . . |
| 4.0 11.0 17.0 22.0 26.0 . . . |
| 5.0 12.0 18.0 23.0 27.0 30.0 . . |
| 6.0 13.0 19.0 24.0 28.0 31.0 33.0 . |
| 7.0 14.0 20.0 25.0 29.0 32.0 34.0 35.0 |
* *
* *
| 16.0 . . . . . . . |
| 38.0 84.0 . . . . . . |
| 60.0 124.0 187.0 . . . . . |
C = | 82.0 164.0 245.0 325.0 . . . . |
| 104.0 204.0 303.0 401.0 498.0 . . . |
| 126.0 244.0 361.0 477.0 592.0 706.0 . . |
| 148.0 284.0 419.0 553.0 686.0 818.0 949.0 . |
| 170.0 324.0 477.0 629.0 780.0 930.0 1079.0 1227.0 |
* *
This example shows the computation C<--alphaABT+alphaBAT+betaC, where A and B are 3 by 5 complex rectangular matrices, and C is a complex symmetric matrix of order 3, stored in lower storage mode.
UPLO TRANS N K ALPHA A LDA B LDB BETA C LDC
| | | | | | | | | | | |
CALL CSYR2K( 'L' , 'N' , 3 , 5 , ALPHA , A , 3 , B , 3 , BETA , C , 4 )
ALPHA = (1.0, 1.0) BETA = (1.0, 1.0)
* *
| (2.0, 5.0) (3.0, 2.0) (4.0, 1.0) (1.0, 7.0) (0.0, 0.0) |
A = | (3.0, 3.0) (8.0, 5.0) (2.0, 5.0) (2.0, 4.0) (1.0, 2.0) |
| (1.0, 3.0) (2.0, 1.0) (6.0, 5.0) (3.0, 2.0) (2.0, 2.0) |
* *
* *
| (1.0, 5.0) (6.0, 2.0) (3.0, 1.0) (2.0, 0.0) (1.0, 0.0) |
B = | (2.0, 4.0) (7.0, 5.0) (2.0, 5.0) (2.0, 4.0) (0.0, 0.0) |
| (3.0, 5.0) (8.0, 1.0) (1.0, 5.0) (1.0, 0.0) (1.0, 1.0) |
* *
* *
| (2.0, 3.0) . . |
C = | (1.0, 9.0) (3.0, 3.0) . |
| (4.0, 5.0) (6.0, 7.0) (8.0, 3.0) |
| . . . |
* *
* *
| (-101.0, 121.0) . . |
C = | (-182.0, 192.0) (-274.0, 248.0) . |
| (-98.0, 146.0) (-163.0, 205.0) (-151.0, 115.0) |
| . . . |
* *
This example shows the computation:
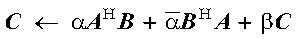
where A and B are 5 by 3 complex rectangular matrices, and C is a complex Hermitian matrix of order 3, stored in upper storage mode.
UPLO TRANS N K ALPHA A LDA B LDB BETA C LDC
| | | | | | | | | | | |
CALL CHER2K( 'U' , 'C' , 3 , 5 , ALPHA , A , 5 , B , 5 , 1.0 , C , 4 )
ALPHA = (1.0, 1.0)
* *
| (2.0, 0.0) (3.0, 2.0) (4.0, 1.0) |
| (3.0, 3.0) (8.0, 0.0) (2.0, 5.0) |
A = | (1.0, 3.0) (2.0, 1.0) (6.0, 0.0) |
| (3.0, 3.0) (8.0, 0.0) (2.0, 5.0) |
| (1.0, 9.0) (3.0, 0.0) (6.0, 7.0) |
* *
* *
| (4.0, 5.0) (6.0, 7.0) (8.0, 0.0) |
| (1.0, 9.0) (3.0, 0.0) (6.0, 7.0) |
B = | (3.0, 3.0) (8.0, 0.0) (2.0, 5.0) |
| (1.0, 3.0) (2.0, 1.0) (6.0, 0.0) |
| (2.0, 0.0) (3.0, 2.0) (4.0, 1.0) |
* *
* *
| (6.0, . ) (3.0, 4.0) (9.0, 1.0) |
C = | . (10.0, . ) (12.0, 2.0) |
| . . (3.0, . ) |
| . . . |
* *
* *
| (102.0, 0.0) (56.0, -143.0) (244.0, -96.0) |
C = | . (174.0, 0.0) (238.0, 78.0) |
| . . (363.0, 0.0) |
| . . . |
* *