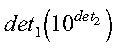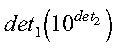Engineering and Scientific Subroutine Library for AIX Version 3 Release 3: Guide and Reference
The SPPFCD and DPPFCD subroutines factor positive definite symmetric matrix
A, stored in lower-packed storage mode, using Gaussian elimination
(LDLT). The reciprocal of the condition number
and the determinant of matrix A can also be computed. To
solve the system of equations with one or more right-hand sides, follow the
call to these subroutines with one or more calls to SPPS or DPPS,
respectively.
The SPOFCD and DPOFCD subroutines factor positive definite symmetric matrix
A, stored in upper or lower storage mode, using Cholesky
factorization (LLT or
UTU). The reciprocal of the condition
number and the determinant of matrix A can also be computed.
To solve the system of equations with one or more right-hand sides, follow the
call to these subroutines with a call to SPOSM or DPOSM, respectively.
To find the inverse of matrix A, follow the call to these
subroutines with a call to SPOICD or DPOICD, respectively.
Table 96. Data Types
| A, aux, rcond, det
| Subroutine
|
| Short-precision real
| SPPFCD and SPOFCD
|
| Long-precision real
| DPPFCD and DPOFCD
|
- Note:
- The output factorization from SPPFCD and DPPFCD should be used only as input
to the solve subroutines SPPS and DPPS, respectively. The output from
SPOFCD and DPOFCD should be used only as input to the following subroutines
for performing a solve or inverse: SPOSM/SPOICD and DPOSM/DPOICD,
respectively.
| Fortran
| CALL SPPFCD | DPPFCD (ap, n, iopt,
rcond, det, aux, naux)
CALL SPOFCD | DPOFCD (uplo, a, lda, n,
iopt, rcond, det, aux, naux)
|
| C and C++
| sppfcd | dppfcd (ap, n, iopt, rcond,
det, aux, naux);
spofcd | dpofcd (uplo, a, lda, n,
iopt, rcond, det, aux,
naux);
|
| PL/I
| CALL SPPFCD | DPPFCD (ap, n, iopt,
rcond, det, aux, naux);
CALL SPOFCD | DPOFCD (uplo, a, lda, n,
iopt, rcond, det, aux,
naux);
|
- uplo
- indicates whether matrix A is stored in upper or lower storage
mode, where:
If uplo = 'U', A is stored in upper
storage mode.
If uplo = 'L', A is stored in lower
storage mode.
Specified as: a single character. It must be 'U' or
'L'.
- ap
- is the array, referred to as AP, in which the matrix
A, to be factored, is stored in lower-packed storage mode.
Specified as: a one-dimensional array of (at least) length
n(n+1)/2+n, containing numbers of the data type
indicated in Table 96.
- a
- is the positive definite symmetric matrix A, to be
factored. Specified as: an lda by (at least) n
array, containing numbers of the data type indicated in Table 96.
- lda
- is the leading dimension of the array specified for a.
Specified as: a fullword integer; lda > 0 and
lda >= n.
- n
- is the order n of matrix A. Specified as:
a fullword integer, where:
For SPPFCD and DPPFCD, n >= 0.
For SPOFCD and DPOFCD,
0 <= n <= lda.
- iopt
- indicates the type of computation to be performed, where:
If iopt = 0, the matrix is factored.
If iopt = 1, the matrix is factored, and the reciprocal of
the condition number is computed.
If iopt = 2, the matrix is factored, and the determinant
is computed.
If iopt = 3, the matrix is factored and the reciprocal of
the condition number and the determinant are computed.
Specified as: a fullword integer; iopt = 0, 1,
2, or 3.
- rcond
- See On Return.
- det
- See On Return.
- aux
- has the following meaning:
If naux = 0 and error 2015 is unrecoverable, aux
is ignored.
Otherwise, is the storage work area used by these subroutines. Its
size is specified by naux. Specified as: an area of
storage, containing numbers of the data type indicated in Table 96.
- naux
- is the size of the work area specified by aux--that is, the
number of elements in aux. Specified as: a fullword
integer, where:
If naux = 0 and error 2015 is unrecoverable, SPPFCD,
DPPFCD, SPOFCD, and DPOFCD dynamically allocate the work area used by the
subroutine. The work area is deallocated before control is returned to
the calling program.
Otherwise, naux >= n.
- ap
- is the transformed matrix A of order n, containing the
results of the factorization. See Function. Returned as: a one-dimensional array of (at
least) length n(n+1)/2+n, containing numbers of the
data type indicated in Table 96.
- a
- is the transformed matrix A of order n, containing the
results of the factorization. See Function. Returned as: a two-dimensional array,
containing numbers of the data type indicated in Table 96.
- rcond
- is the estimate of the reciprocal of the condition number, rcond,
of matrix A. Returned as: a number of the data type
indicated in Table 96; rcond >= 0.
- det
- is the vector det, containing the two components
det1 and det2 of the determinant of
matrix A. The determinant is:
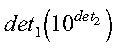
where 1 <= det1 < 10.
Returned as: an array of length 2, containing numbers of the data type
indicated in Table 96.
- All subroutines accept lowercase letters for the uplo
argument.
- In your C program, argument rcond must be passed by
reference.
- When iopt = 0, SPPFCD and DPPFCD provide the same
function as a call to SPPF or DPPF, respectively. When
iopt = 0, SPOFCD and DPOFCD provide the same function as a
call to SPOF or DPOF, respectively.
- SPPFCD and DPPFCD in many cases utilize new algorithms based on recursive
packed storage format. As a result, on output, the array specified for
AP may be stored in this new format rather than the conventional lower packed
format. (See references [52], [66], and [67]).
The array specified for AP should not be altered between calls to the
factorization and solve subroutines; otherwise unpredictable results may
occur.
- See Notes for information on specifying a value for iopt in
the SPPS and DPPS subroutines after calling SPPFCD and DPPFCD,
respectively.
- In the input and output arrays specified for ap, the first
n(n+1)/2 elements are matrix elements. The additional
n locations in the array are used for working storage by this
subroutine and should not be altered between calls to the factorization and
solve subroutines.
- For a description of how a positive definite symmetric matrix is stored in
lower-packed storage mode in an array, see Symmetric Matrix. For a description of how a positive definite
symmetric matrix is stored in upper or lower storage mode, see Positive Definite or Negative Definite Symmetric Matrix.
- You have the option of having the minimum required value for naux
dynamically returned to your program. For details, see Using Auxiliary Storage in ESSL.
The functions for these subroutines are described in the sections
below.
The positive definite symmetric matrix A, stored in lower-packed
storage mode, is factored using Gaussian elimination, where A is
expressed as:
- A = LDL T
where:
- L is a unit lower triangular matrix.
- LT is the transpose of matrix L.
- D is a diagonal matrix.
An estimate of the reciprocal of the condition number, rcond, and
the determinant, det, can also be computed by this
subroutine. The estimate of the condition number uses an enhanced
version of the algorithm described in references [69] and [70].
If n is 0, no computation is performed. See references
[36] and [38].
These subroutines call SPPF and DPPF, respectively, to perform the
factorization using Gaussian elimination (LDLT).
If you want to use the Cholesky factorization method, you must call SPPF and
DPPF directly.
The positive definite symmetric matrix A, stored in upper or
lower storage mode, is factored using Cholesky factorization, where
A is expressed as:
- A = LL T or
A = UTU
where:
- L is a lower triangular matrix.
- LT is the transpose of matrix L.
- U is an upper triangular matrix.
- UT is the transpose of matrix U.
If specified, the estimate of the reciprocal of the condition number and
the determinant can also be computed. The estimate of the condition
number uses an enhanced version of the algorithm described in references
[69] and [70].
If n is 0, no computation is performed. See references
[8] and [36].
Error 2015 is unrecoverable, naux = 0, and unable to
allocate work area.
- Matrix A is not positive definite (for SPPFCD and
DPPFCD).
- If matrix A is singular (at least one of the diagonal elements
are 0), then rcond and det, if you requested them, are set
to 0.
- If matrix A is nonsingular and nonpositive definite (none of
the diagonal elements are 0 and at least one diagonal element is negative),
then rcond and det, if you requested them, are
computed.
- One or more elements of D contain values less than or equal to
0; all elements of D are checked. The index i
of the last nonpositive element encountered is identified in the computational
error message, issued by SPPF or DPPF, respectively.
- i can be determined at run time by using the ESSL error-handling
facilities. To obtain this information, you must use ERRSET to change
the number of allowable errors for error code 2104 in the ESSL error option
table; otherwise, the default value causes your program to be terminated
by SPPF or DPPF, respectively, when this error occurs. If your program
is not terminated by SPPF or DPPF, respectively, the return code is set to
2. For details, see What Can You Do about ESSL Computational Errors?.
- Matrix A is not positive definite (for SPOFCD and
DPOFCD).
- If matrix A is singular (at least one of the diagonal elements
are 0), then rcond and det, if you requested them, are set
to 0.
- If matrix A is nonsingular and nonpositive definite (none of
the diagonal elements are 0 and at least one diagonal element is negative),
then rcond and det, if you requested them, are
computed.
- Processing stops at the first occurrence of a nonpositive definite
diagonal element.
- The order i of the first minor encountered having a
nonpositive determinant is identified in the computational error
message.
- i can be determined at run time by using the ESSL error-handling
facilities. To obtain this information, you must use ERRSET to change
the number of allowable errors for error code 2115 in the ESSL error option
table; otherwise, the default value causes your program to be terminated
by SPPF or DPPF, respectively, when this error occurs. If your program
is not terminated by SPPF or DPPF, respectively, the return code is set to
2. For details, see What Can You Do about ESSL Computational Errors?.
- uplo <> 'U' or 'L'
- lda <= 0
- lda < n
- n < 0
- iopt <> 0, 1, 2, or 3
- Error 2015 is recoverable or naux<>0, and naux is
too small--that is, less than the minimum required value. Return
code 1 is returned if error 2015 is recoverable.
This example computes the factorization, reciprocal of the condition
number, and determinant of matrix A. The input is the same
as used in Example 1 for SPPF.
The values used to estimate the reciprocal of the condition number are
obtained with the following values:
- ||A||1 = max(9.0,
17.0, 24.0, 30.0, 35.0, 39.0, 42.0,
44.0, 45.0) = 45.0
- Estimate of ||A|| = 4.0
On output, the value in det, |A|, is equal to
1.
AP N IOPT RCOND DET AUX NAUX
| | | | | | |
CALL DPPFCD( AP , 9 , 3 , RCOND , DET , AUX , 9 )
AP =(same as input AP in
Example 1)
AP =(same as output AP in Example 1)
RCOND = 0.0055555
DET = (1.0, 0.0)
This example computes the factorization, reciprocal of the condition
number, and determinant of matrix A. The input is the same
as used in Example 3 for SPOF.
The values used to estimate the reciprocal of the condition number are
obtained with the following values:
- ||A||1 = max(9.0,
17.0, 24.0, 30.0, 35.0, 39.0, 42.0,
44.0, 45.0) = 45.0
- Estimate of ||A|| = 4.0
On output, the value in det, |A|, is equal to
1.
UPLO A LDA N IOPT RCOND DET AUX NAUX
| | | | | | | | |
CALL SPOFCD( 'L', A , 9 , 9 , 3 , RCOND , DET , AUX , 9 )
A =(same as input A in
Example 3)
A =(same as output A in Example 3)
RCOND = 0.0055555
DET = (1.0, 0.0)
This example computes the factorization, reciprocal of the condition
number, and determinant of matrix A. The input is the same
as used in Example 4 for SPOF.
The values used to estimate the reciprocal of the condition number are
obtained with the following values:
- ||A||1 = max(9.0,
17.0, 24.0, 30.0, 35.0, 39.0, 42.0,
44.0, 45.0) = 45.0
- Estimate of ||A|| = 4.0
On output, the value in det, |A|, is equal to
1.
UPLO A LDA N IOPT RCOND DET AUX NAUX
| | | | | | | | |
CALL SPOFCD( 'U', A , 9 , 9 , 3 , RCOND , DET , AUX , 9 )
A =(same as input A in
Example 4)
A =(same as output A in Example 4)
RCOND = 0.0055555
DET = (1.0, 0.0)
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page | Table of Contents | Index ]