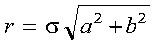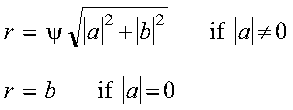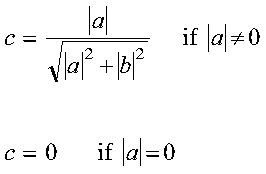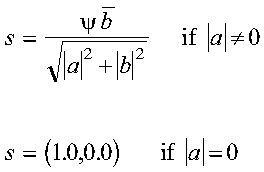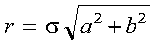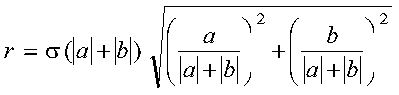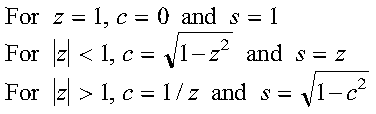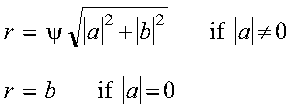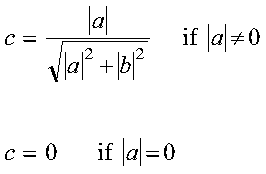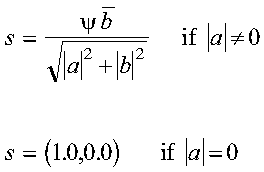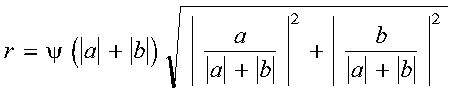Engineering and Scientific Subroutine Library for AIX Version 3 Release 3: Guide and Reference
SROTG and DROTG construct a real Givens plane rotation, and CROTG and ZROTG
construct a complex Givens plane rotation. The computations use
rotational elimination parameters a and b. Values are
returned for r, as well as the cosine c and the sine
s of the angle of rotation. SROTG and DROTG also return a
value for z.
- Note:
- Throughout this description, the symbols r and z are used
to represent two of the output values returned for this computation. It
is important to note that the values for r and z are
actually returned in the input-output arguments a and b,
respectively, overwriting the original values passed in a and
b.
Table 48. Data Types
| a, b, r, s
| c
| z
| Subprogram
|
| Short-precision real
| Short-precision real
| Short-precision real
| SROTG
|
| Long-precision real
| Long-precision real
| Long-precision real
| DROTG
|
| Short-precision complex
| Short-precision real
| (No value returned)
| CROTG
|
| Long-precision complex
| Long-precision real
| (No value returned)
| ZROTG
|
| Fortran
| CALL SROTG | DROTG | CROTG | ZROTG (a, b, c,
s)
|
| C and C++
| srotg | drotg | crotg | zrotg (a, b, c,
s);
|
| PL/I
| CALL SROTG | DROTG | CROTG | ZROTG (a, b, c,
s);
|
- a
- is the rotational elimination parameter a. Specified
as: a number of the data type indicated in Table 48.
- b
- is the rotational elimination parameter b. Specified
as: a number of the data type indicated in Table 48.
- c
- See On Return.
- s
- See On Return.
- a
- is the value computed for r.
For SROTG and DROTG:
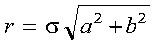
where:
- sigma = SIGN(a) if |a| > |b|
- sigma = SIGN(b) if |a| <= |b|
For CROTG and ZROTG:
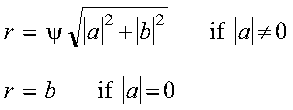
where:
- psi = a/|a|
Returned as: a number of the data type indicated in Table 48.
- b
- is the value computed for z.
For SROTG and DROTG:
- z = s if
|a| > |b|
- z = 1/c if
|a| <= |b| and c <> 0 and
r <> 0
- z = 1 if
|a| <= |b| and c = 0 and
r <> 0
- z = 0 if r = 0
For CROTG and ZROTG: no value is returned, and the input value is not
changed.
Returned as: a number of the data type indicated in Table 48.
- c
- is the cosine c of the angle of (Givens) rotation. For
SROTG and DROTG:
- c = a/r if
r <> 0
- c = 1 if r = 0
For CROTG and ZROTG:
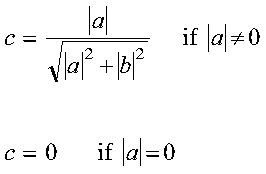
Returned as: a number of the data type indicated in Table 48.
- s
- is the sine s of the angle of (Givens) rotation.
For SROTG and DROTG:
- s = b/r if
r <> 0
- s = 0 if r = 0
For CROTG and ZROTG:
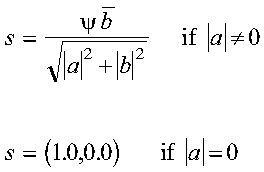
where psi = a/|a|
Returned as: a number of the data type indicated in Table 48.
In your C program, arguments a, b, c, and
s must be passed by reference.
A real Givens plane rotation is constructed for values a and
b by computing values for r, c, s, and z,
where:
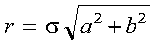
where:
- sigma = SIGN(a) if
|a| > |b|
- sigma = SIGN(b) if
|a| <= |b|
c = a/r if
r <> 0
c = 1 if r = 0
s = b/r if
r <> 0
s = 0 if r = 0
z = s if
|a| > |b|
z = 1/c if
|a| <= |b| and c <> 0 and
r <> 0
z = 1 if |a| <= |b|
and c = 0 and r <> 0
z = 0 if r = 0
See reference [79].
Following are some important points about the computation:
- The numbers for c, s, and r satisfy:
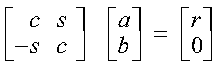
- Where necessary, scaling is used to avoid overflow and destructive
underflow in the computation of r, which is expressed as
follows:
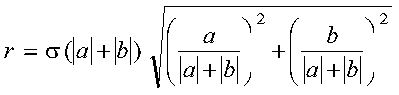
- sigma is not essential to the computation of a Givens rotation matrix, but
its use permits later stable reconstruction of c and s from
just one stored number, z. See reference [91]. c and s are reconstructed
from z as follows:
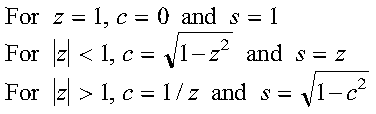
A complex Givens plane rotation is constructed for values a and
b by computing values for r, c, and s, where:
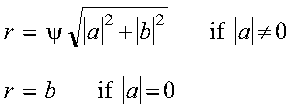
where:
- psi = a/|a|
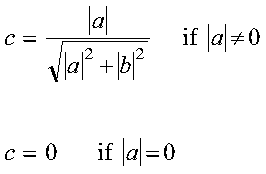
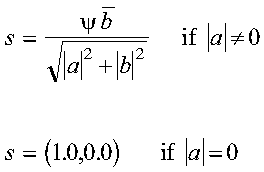
See reference [79].
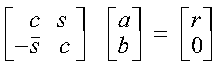
Following are some important points about the computation:
- The numbers for c, s, and r satisfy:
- Where necessary, scaling is used to avoid overflow and destructive
underflow in the computation of r, which is expressed as
follows:
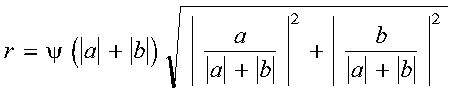
None
None
This example shows the construction of a real Givens plane rotation, where
r is 0.
A B C S
| | | |
CALL SROTG( 0.0 , 0.0 , C , S )
A = 0.0
B = 0.0
C = 1.0
S = 0.0
This example shows the construction of a real Givens plane rotation, where
c is 0.
A B C S
| | | |
CALL SROTG( 0.0 , 2.0 , C , S )
A = 2.0
B = 1.0
C = 0.0
S = 1.0
This example shows the construction of a real Givens plane rotation, where
|b| > |a|.
A B C S
| | | |
CALL SROTG( 6.0 , -8.0 , C , S )
A = -10.0
_
B = -1.666
C = -0.6
S = 0.8
This example shows the construction of a real Givens plane rotation, where
|a| > |b|.
A B C S
| | | |
CALL SROTG( 8.0 , 6.0 , C , S )
A = 10.0
B = 0.6
C = 0.8
S = 0.6
This example shows the construction of a complex Givens plane rotation,
where |a| = 0.
A B C S
| | | |
CALL CROTG( A , B , C , S )
A = (0.0, 0.0)
B = (1.0, 0.0)
A = (1.0, 0.0)
C = 0.0
S = (1.0, 0.0)
This example shows the construction of a complex Givens plane rotation,
where |a| <> 0.
A B C S
| | | |
CALL CROTG( A , B , C , S )
A = (3.0, 4.0)
B = (4.0, 6.0)
A = (5.26, 7.02)
C = 0.57
S = (0.82, -0.05)
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page | Table of Contents | Index ]